This gallery contains 2 photos.
American Journal of Psychiatry, 2013. March. 170(3): 275-89. This paper is a review of dietary and psychological treatments for ADHD. QUOTE (Conclusion): “Free fatty acid supplementation and artificial food color exclusions appear to have beneficial effects on ADHD symptoms, although … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
We already know too much sugar is bad for you ………but ARTIFICIAL sugar may be worse. Click on the picture to see a short but important video from an article in TIME Related studies: (Get password) Azad 2016 — Association … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 2013 Jan 4;6:344. This is a review of evidence suggesting that a gluten-free diet, a casein-free diet (or both) are helpful for people on the autism spectrum. QUOTE: “Although not wholly affirmative, the majority of published … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Pediatrics, 2012 Feb;129(2): 330-7. Millichap says his article is a comprehensive overview of the role of diet for treatment of children with ADHD “when pharmacotherapy has proven unsatisfactory or unacceptable.” He promises to talk about new research. Unfortunately, he falls … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Lebanese American University, Masters Thesis 2012 In a project for her Masters Degree in Education, Linda Saab performed a case study on a 9 year old boy in Beirut who was diagnosed with ADHD. Although he was observed for 5 … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 4 photos.
The Lancet, 2011. Feb 5;377 (9764): 494-503 This is a study of 100 children diagnosed with ADHD but not selected on any basis of expectation of a dietary effect. The children were randomly assigned to an experimental diet group and … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
American Journal of Psychiatry. 2010 Sep;167(9): 1108-15 Stevenson analyzed the reactions of children in the McCann (2007) study to see why not all children react to additives in the same way. He found that variation in several genes that control … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
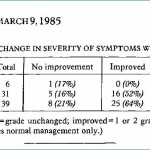
European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 2009 Jan;18(1):12-9. In a randomized controlled trial in the Netherlands, 27 children were assigned either to an elimination diet or to a “waiting list” control group for 5 weeks, beginning after a 2-week “baseline” diet … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Lancet, September 6, 2007 As a followup to the earlier Bateman (2004) study, the authors retested 153 toddlers as well as 144 elementary school (8/9 years old) children from the general population. They were briefly put on a dye-free … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Food Additives & Contaminants, 2006. Mar; 23(3): 245-51. Husain evaluated the amount of food dyes consumed by children in 58 schools in Kuwait, and found that the amounts of four of the colors were 4 to 8 times above the … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Allergology International, 2006. Jun; 55(2):203-5. This is a case report about a 5-year-old girl in Japan with multiple recurrent problems: urticaria (hives), angioedema (swelling), headaches, dyspnea (shortness of breath), loss of consciousness, and abdominal pain. Her symptoms were made worse … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 3 photos.
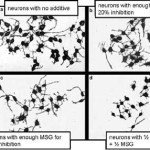
Toxicological Sciences. 2006 Mar; 90(1):178-87. This is one of the few studies examining and comparing the neurotoxic activity of food additives alone and in combination. After determining how much of each additive reduces neurite development by 20%, Lau combined pairs … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Journal of Attention Disorders, 2006. Nov;10(2):200-4. Because several studies had reported a possible association of celiac disease (CD) and ADHD symptoms, the authors evaluated 132 participants diagnosed with CD – both children and adults – for ADHD symptoms before they … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health, 2002. Aug;38(4):373-6 In Australia, 27 children whose behavior had improved on the Royal Prince Alfred Hospital diet were enrolled in a double-blind placebo-controlled test of the bread preservative calcium propionate (preservative code 282). More … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Nederlandsch tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 2002, Dec 28;146(52):2543-7. 36 boys and 4 girls, diagnosed with ADHD, were put on an oligoantigenic (few foods – rice, turkey, pear and lettuce) diet for two weeks. 9 children (23%) withdrew from the study because of … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
For those who may be wondering about the lack of newly posted studies on here over the past few weeks, I just want to let you know I did not drop out of sight …. exactly. I have found a … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 3 photos.
Annales Academiae Medicae Stetinensis, 1998;44:297-314 Deficiencies of magnesium, copper, zinc, calcium, and iron occur more in children with ADHD, and magnesium deficiency is the most frequent. Starobrat-Hermelin studied a group of 110 hyperactive children who also had a variety … Continue reading →
Below are some of the members of the Nutrition Foundation in the 1970’s. This was the group that designed and funded early studies to determine the credibility of the Feingold diet. Officers and Trustees of the Nutrition Foundation at that … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 1997. Jun;6(2):88-95. Fig. 1 Study design Schmidt compared the effectiveness of an oligoantigenic (few foods) diet with Ritalin for hyperactive disruptive children (today called conduct disorder). 44% responded to Ritalin while 24% responded equally well … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Food Additives and Contaminants, 1996. Jan;13(1):5-11 In this lab study, 11 artificial food dyes – not all of them used in the US — were tested to determine their effect on the mitochondria of rat liver and kidney. NOTE: Mitochondria … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Annals of Allergy, May 1994, Vol. 72, pp. 462-8. 73% of 26 children with ADHD responded favorably to a diet eliminating reactive foods and artificial colors. 16 of the improved children were given a double blind challenge with 100 mg … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Journal of Pediatrics, November 1994, Vol. 135, pp.691-8 150 of 200 children [75%] improved on an open trial of a diet free of synthetic food coloring, and deteriorated upon introduction of foods containing synthetic colorings. 34 other “clear” or “suspected” … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Archives of Disease in Childhood, November 1993, Vol. 69 (5), pp.564-8 59 of 78 children (75.6%) referred for “hyperactive behavior” improved on an open trial of an elimination diet. 19 of them were studied in a placebo-controlled double-blind challenge protocol. … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Pediatria Medica e Chirurgica 1992 Jan-Feb;14(1):39-42 The author describes two cases of reactions to the food additives tartrazine (Yellow 5) and benzoates involving mainly the central nervous system (headache, migraine, overactivity, concentration and learning difficulties, depression) and joints (arthralgias), confirmed … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Pollock & Warner, Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1990. Jan;65(1):74-7, Heart and Lung Institute, Brompton Hospital, London. Pollock did a double-blind placebo-controlled challenge study on 19 children who had improved previously on an additive-free diet. He didn’t use any additives … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Proceedings of the Nutrition Society of Australia, 1990 pg. 233. Sarantinos studied 13 children, 4-14 years old, who had been at least 6 weeks on a diet free of synthetic food dyes as part of their treatment for ADHD. The … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Journal of Nutritional Medicine; 1 (1). 1990. 51-58. Ward first studied the zinc status in various tissues (blood, hair, saliva, etc) in 20 hyperactive boys compared to 20 non-hyperactive boys. Then, in a double-blind placebo-controlled study of 10 hyperactive boys … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Journal of Pediatrics, 1989. Jan;114(1):51-8. Egger put 45 children with epilepsy and recurrent headaches, abdominal symptoms, or hyperactivity on an oligoantigenic (few foods) diet. 36 of them — 80% — improved. QUOTE: “Headaches, abdominal pains, and hyperkinetic behavior ceased … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Australian Paediatric Journal, April 1988, Vol. 24 (2), pp. 143-7 Of 220 children referred for suspected hyperactivity, 55 were put on a 6-week trial of the Feingold Diet. 40 of them — 72.7% — exhibited improved behavior, and 26 of … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1987. Feb;62(2):119-22. In a double-blind study, David challenged 24 of his patients who had been using diet for ADHD with benzoic acid (a preservative) and a large dose of coloring — 250 mg of Yellow … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 3 photos.
Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 1987. Jan;26(1):53-5. Gross carried out a diet study in a summer camp which is a great way to totally control the diet and get solid results in a study. NOTE: … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 4 photos.
International Journal for Biosocial Research, 1986, 8(2); 185-195. Over 4 years, 803 New York City schools changed their breakfast and lunch programs. They lowered sucrose, synthetic food color/flavors, and two preservatives (BHA and BHT). For each change, there was an … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
The Lancet, 9;1(8428):540-5. 62 of 76 (81.6%) overactive children improved by at least one grade level on an oligoantigenic (few foods) diet. Benzoic acid and tartrazine (Yellow 5) were the most common problems, but all children had other sensitivities as … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Journal of Learning Disabilities, 1983. Jun-Jul;16(6):319-23. Mattes gives his opinion that improvement on the Feingold diet is “based on anecdotal evidence;” he claims that the studies show the diet “is probably not effective, except perhaps in a very small percentage … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Neurobehavioral Toxicology and Teratology, 1982. Jan-Feb;4(1): 43-9. Goldenring studied the effects of giving sulfanilic acid to rat pups. He chose this chemical because it is formed when azo food dyes are digested. He gave the sulfanilic acid to normal rat … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
International Journal of Neuroscience, 1982. May;16(3-4):241-246 QUOTE: “… The physiological measures [EEG and heart rate] were obtained prior to and following the ingestion of drinks containing food additives or placebos, which were administered in a double-blind, randomized, crossover procedure. … … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Mattes & Gittelman, Archives of General Psychiatry. 1981. June; 38(6): 714-8 Mattes claimed he tried to maximize the behavioral effects of artificial food dyes by (1) studying only children already on the Feingold diet, (2) trying to exclude placebo responders, … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Science, March 28, 1980, Vol. 207. pp.1485-7 QUOTE: “The performance of the hyperactive children on paired-associate learning tests on the day they received the dye blend was impaired relative to their performance after they received the placebo, but the performance … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
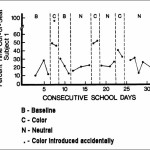
Science, 1980. March 28;207 (4438): 1487-9. QUOTE: ”Twenty-two young children, maintained on a diet that excluded certain foods, were challenged intermittently with a blend of seven artificial colors in a double-blind trial. Parents’ observations provided the criteria of response. One … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 1979. Vol 23(1) 73-84. QUOTE: “This disenchantment with present-day rehabilitation techniques prompted the Ford Foundation in its annual report for 1977 to recommend that the role in delinquency of biochemical and organic … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Science. 1979. July 27; 205 (4404): 410-2. Lafferman found that erythrosin B [Red 3] given to rats prevents the uptake of dopamine (the “feel good” neurotransmitter) by nerve cells in the brain called the caudate synaptosomes. This is consistent with … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Neurobehavioral Toxicology, 1979. Spring;1(1):41-7. (Today called Neurotoxicology and Teratology) In a study on rat pups, the highest dose of food dyes caused the greatest activity. Even after a half hour, the pups only calmed down by 7.25% — while the … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Medical Journal of Australia, 1978 Dec 2;2(12):548, 569-70. The Feingold diet, as used in Australia, was found to be nutritionally superior to a “normal” diet, and pronounced safe to use. MedLine
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Medical Journal of Australia, 1978. Dec 2;2(12):570-2 To test for reactions to salicylate, 12 children who had been on the Feingold diet for about a year were challenge-tested with 40 mg of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) in a double-blind, cross-over trial … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Pediatrics, 1978. Jun;61(6):818-28 In a double-blind diet study in which all food was provided for a “Feingold Diet” and a “control diet,” parents of 63% of the 36 school-age children and 100% of the 10 preschool children reported improved behavior … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 1978 Nov;73(5):515-9 Harper calculated the nutrient intake of 54 children before and on the Feingold diet. They were as good or better than the Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) — in other words, the … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
New Zealand Medical Journal, 1978. Jul 26;88(616):43-5. QUOTE: “Ten hyperkinetic children have been treated with the [Feingold] diet, five of whom improved dramatically and are now off all other therapy. Their response to accidental and deliberate challenge supports the hypothesis … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis 1978 Winter; 11(4):439-46 This was a double-blind study on two girls who had been on the Feingold diet for almost a year. Trained observers watched them in school and reported on the frequency of the … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 1 photo.
Pediatrics. 1978 Jun;61(6):811-7. 26 hyperactive children were given a “modified” Feingold diet in which artificial food dyes and flavorings were eliminated, but not preservatives or salicylates. They were then challenged in four ways: Cookie with 13 mg food dyes + … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Clinical Pediatrics (Phila) 1977 Jul;16(7):652-6 (Case studies) When 32 hyperactive children Dr. Brenner had been treating medically for years were given the Feingold diet, 11 of them — 34.3% — “markedly improved.“ Another 2 improved as much but were older, … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Journal of the American Society for Preventive Dentistry, 1977 Jan-Feb;7(1):13-5. QUOTE: “The presence of food additives in products used in dental procedures may have serious consequences for many patients. Hyperactivity and learning disabilities as well as buccal, gingival and … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Speech to American Academy of Pediatrics, New York Hilton Hotel, November 8, 1977. QUOTE: ”Recognizing that any compound under the appropriate conditions can induce adverse reactions, including behavioral disturbances, it becomes necessary to evaluate each compound or class of compounds … Continue reading →
This gallery contains 2 photos.
Journal of Learning Disabilities, November 1976 vol.9 no.9 p.560-569 Spring reviewed the few studies available at that time and concluded that there was no “epidemic” of hyperactivity in the 1970s because a particular WISC reading score average was higher in … Continue reading →
For doctors, students, researchers, and parents. I have been collecting the research studies related to diet, behavior and health for over 30 years. Download My Science Library for your information and convenience. It has been updated February 17, 2024, is … Continue reading →
In the 1970s and early 1980s, my son Zohar was miserable and unmanageable. The doctor prescribed Ritalin to “fix the imbalance in his brain.” We began with Ritalin and progressed through all the medications then available, including one now removed … Continue reading →