This gallery contains 3 photos.
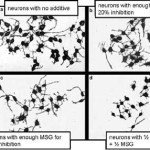
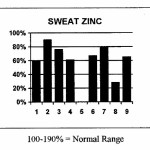
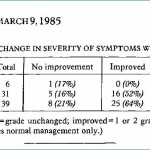
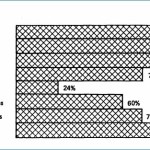
Toxicological Sciences. 2006 Mar; 90(1):178-87. This is one of the few studies examining and comparing the neurotoxic activity of food additives alone and in combination. After determining how much of each additive reduces neurite development by 20%, Lau combined pairs … Continue reading